Spoiler: It’s probably not your biceps, abs, or even your heart.
The human body is a marvel—built from bones, muscles, and intricate blood vessels. But here’s the burning question: What is the most important muscle in the human body?
Let’s unpack the answer. It’ll surprise you.
The 6 Most Important Muscles in Your Body
1. Heart (Cardiac Muscle)
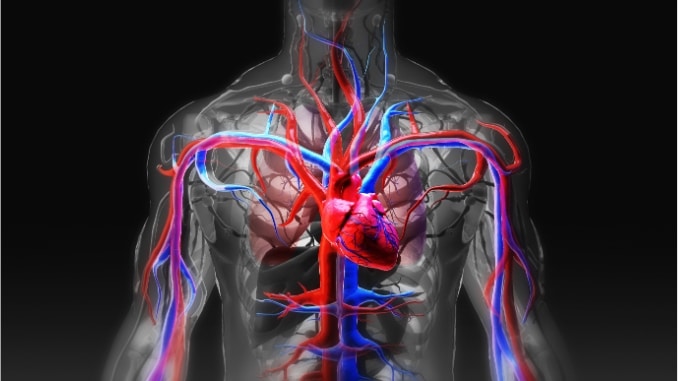
This involuntary muscle never stops working. Your heart pumps 24/7, supplying oxygenated blood to fuel all your muscles and body functions.
2. Gluteus Maximus
The largest muscle in your body, it stabilizes your hip joint, powers walking and running, and even protects your lower back.
3. Hip Flexors
These deep-core muscles affect posture, mobility, and even digestion. Tight or weak hip flexors can lead [1] to muscle pain, back issues, and poor athletic performance.
4. Latissimus Dorsi
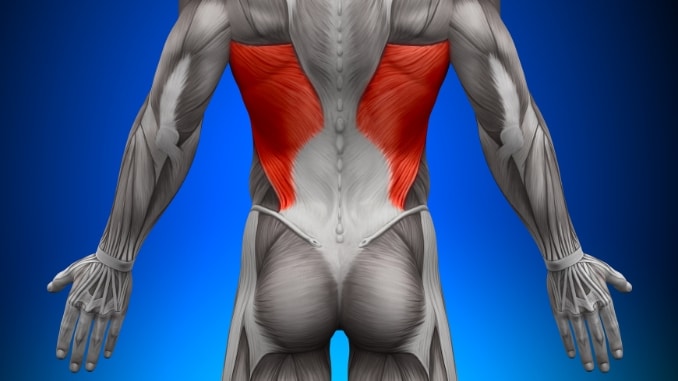
A major player in upper-body pulling movements. It helps lift heavy objects, supports posture, and connects muscles from your spine to your arms.
5. Rectus Abdominis
Your “six-pack” muscles [2]. These maintain posture and allow for trunk movement. They also protect internal organs.
6. Biceps Brachii
Often overhyped, but critical for arm movement [3], lifting, and stabilizing the shoulder blade during pulling actions.
What Is the Most Important Muscle in the Body?
According to leading fitness physiologists, the hip flexors may take the crown.
Often referred to as your “hidden survival muscle,” the hip flexors are crucial for:
- Reducing back pain and joint strain
- Improving posture
- Enhancing athletic performance
- Improving posture, mobility, and energy levels
When they’re tight or inactive, your entire muscular system suffers. But when properly engaged and trained, they unlock true strength, balance, and longevity.
The 3 Types of Muscles in the Human Body
To truly appreciate the most important muscle, you need to know the types of muscle tissue:
- Skeletal Muscles – Voluntary, striated muscles like your quads, glutes, and biceps. These are responsible for movement, posture, and generating maximum force.
- Smooth Muscles – Found in internal organs like your intestines and blood vessels. These involuntary muscles move food, control blood flow, and regulate internal body functions.
- Cardiac Muscle – Found only in your heart, it’s the hardest working muscle—constantly moving without rest. It’s responsible for keeping you alive. No big deal.
What’s the Strongest Muscle in the Human Body?

Depends on how you define “strong”:
- Jaw (Masseter): Capable of generating the greatest force relative to its size, especially in biting.
- Heart: The most endurance-capable and resilient.
- Gluteus Maximus: Delivers the greatest force output.
- Tongue: Arguably the most versatile in motion and function.
So when someone asks what muscle is strongest… ask them: “In what way?”
How to Train for Skiing: Build the Right Muscles
Whether you’re a seasoned skier or planning your first downhill trip, training the right muscle groups is critical to avoid muscle injuries, swelling, or poor performance.
Best Exercises Before Skiing:
- Hip Extension Work – Target the glutes, hamstrings, and hip flexors
- Core Stabilization – Engage your rectus abdominus and obliques for balance
- Leg Endurance – Squats, lunges, and wall-sits prep your knee joint and leg muscles
- Shoulder & Upper Body Mobility – Protects your shoulder blade and arms during pole use
Stretching is a must to keep your joints, tendons, and muscles resilient to impact.
Expert Insight: What Do Professionals Say?
“The hip flexors are underestimated. In clinical rehab, I’ve seen how unlocking them reverses posture issues, reduces pain, and even enhances breathing.” – Dr. Brian Abelson, DC, Certified Kinesiologist (Calgary, Alberta)
Though Canadian-based, his training methods are widely used across the U.S. and endorsed by American sports rehab specialists.
Final Thought: Why It All Matters
With over 600 muscles in the body, it’s easy to ignore the ones working silently beneath the surface. But your muscles work all day—supporting your posture, aiding movement, and maintaining health. From the skin to the head, every part of you is interconnected.
Embrace healthy behaviors, strengthen your muscular system, and don’t underestimate the power of your hip flexors.
Bonus: How Many Muscles Are in the Human Body? There are over 600 muscles in the body. Including individual muscle fibers, tendon junctions, and connective tissues, the number becomes significantly larger.
For your guide to unlocking your tight hip flexors, check out Unlock Your Hip Flexors here!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most important muscle in the human body?
While many believe it’s the heart or glutes, recent insights point to the hip flexors as the most vital for overall movement, posture, and performance. When healthy, they reduce back pain and boost full-body function.
How many muscles are in the human body?
The average human body contains over 600 muscles, including skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles. If you count all the individual muscle fibers, the total is even higher.
What’s the difference between skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles?
- Skeletal muscles: Voluntary muscles attached to bones—used in movement.
- Smooth muscles: Involuntary muscles in organs and blood vessels.
- Cardiac muscle: The specialized muscle found only in the heart.
What’s the strongest muscle in terms of absolute force?
The masseter (jaw muscle) can exert the most absolute strength. However, muscles like the gluteus maximus, tongue, and heart all rank high depending on how you define “strong.”
What are the best exercises to prevent muscle injuries before skiing?
Focus on warming up your hip joint, knee joint, and core. Include dynamic stretches, glute activation, and balance drills to protect your muscle groups and avoid common muscle injuries.